To provide the innovative research and diagnostic products for improving prevention and treatment of thrombotic and hemorrhagic complications, we are creating the technology for dissecting the distinct mechanisms for the active form of FX (FXa) generation in an initiation phase of blood coagulation.
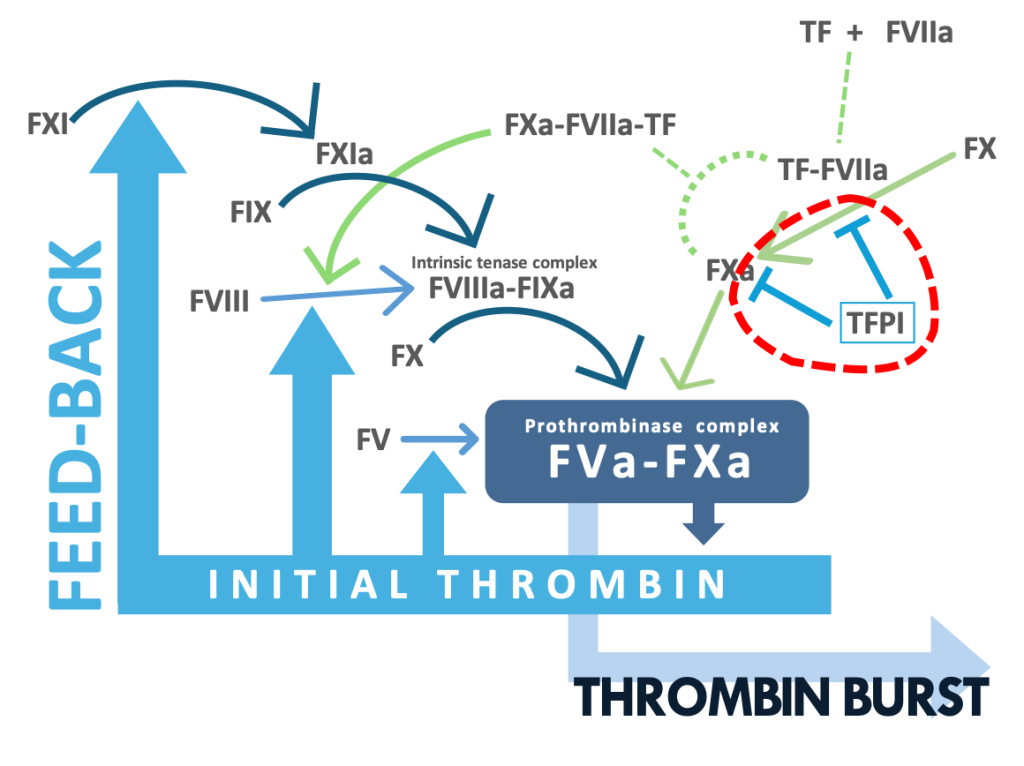
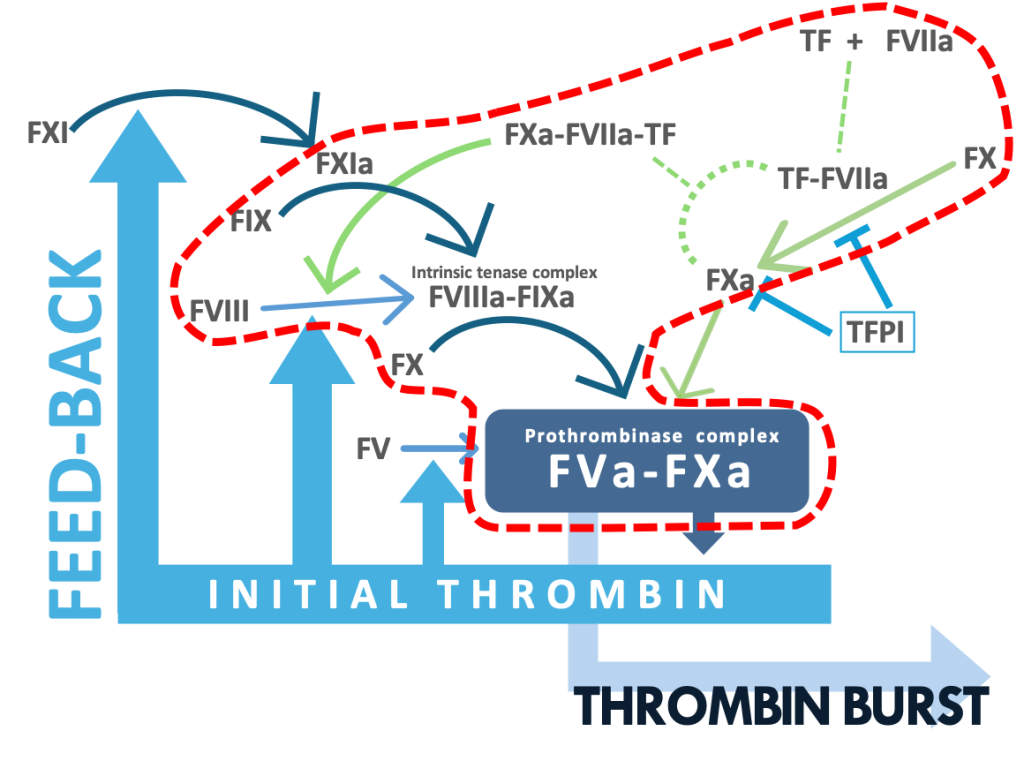
Blood coagulation is a key for hemostasis in response to tissue injury, but also contributes to thrombosis. FXa has a crucial role in blood coagulation: FXa forms prothrombinase complex by binding to its active cofactor FVa and the complex activates prothrombin to an active enzyme thrombin. Thrombin produces stable clots and plugs by activation of platelets and fibrin formation. To date, direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) targeting FXa are widely used for treating patients with stroke and venous thrombosis. Despite the excellent antithrombotic profile, there still remain unmet needs for reducing bleeding complications. Safer therapy with DOACs requires more understanding of the mechanisms of the FXa generation that contribute to thrombosis but have lesser impact on hemostasis.
In the current concept, the tissue factor (TF) complex with the active form of FVII (FVIIa) converts FX to FXa by the proteolytic activation of FX. After being released from the FVIIa-TF complex, FXa functions as a proteolytic enzyme such as prothrombin activation. The recent study has provided a novel insight into the activity of FXa: the nascent product FXa of FVIIa-TF, which is in the ternary complex of FXa-FVIIa-TF albeit the temporary complex, has a proteolytic activity since FXa still bound to FVIIa-TF activates protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR-2) expressed on a cell membrane by a limited proteolysis (Blood 130:1604-1605, 2017).
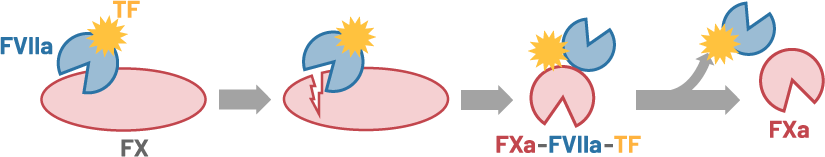
FXa is also generated by the proteolytic activation of FX with the active form of FIX (FIXa).
The FIXa activation of FX requires the active form of FVIII (FVIIIa), a cofactor of FIXa.
In the current schema on blood coagulation, it is believed that FVIIIa is generated by the thrombin activation of FVIII and that the FXa generation by FIXa-FVIIIa contributes to the amplification of blood coagulation not to initiation, leading to thrombin burst.
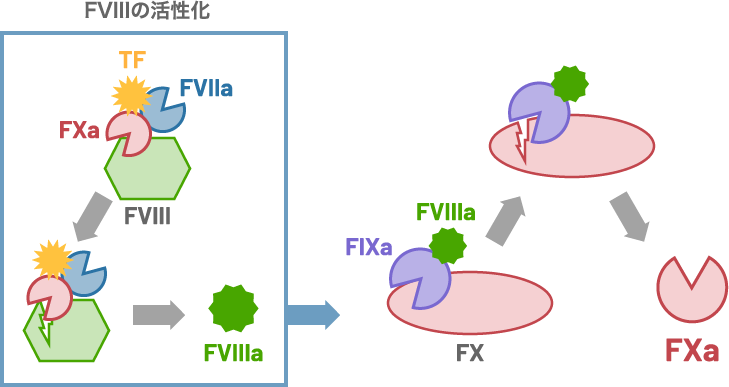
More recently performed studies, however, have indicated involvement of the TF pathway products in the activation of FVIII.
Given evidence that the FVIIa-TF complex generates FIXa , it is highly likely that the FXa generation by FIXa-FVIIIa occurs in an initiation phase of coagulation.
Selective factor VIII activation by the tissue factor-factor VIIa-factor Xa complex. Blood.130(14):1661-1670, 2017
Schematic illustration of the activation of FVIII
by FXa still bound to the FVIIa-TF complex and the generation of FXa by FIXa-FVIIIa

Development of the highly sensitive blood coagulation test
“SMAT®” kits
The novel thrombin production assays
Based on the discovery of the novel coagulation mechanism, we have established the assays with very high sensitivity for determining the initial small amounts of thrombin that are here indicated as "SMAT®": SMAT®-FVIII/IX is for the thrombin production via the FIXa-FVIIIa mechanism by which FVIII is activated by the FXa-FVIIa-TF complex; SMAT®-TF is for the thrombin production via the FVIIa-TF pathway.
The SMAT®-TF kit is utilized for specifically determining the TF-driven thrombin production independently of FVIII activation. The kit includes anti-FVIII antibody blocking the FVIIIa activity. The kit may provide an excellent approach for accessing hypercoagulable state and thrombosis caused by the FVIIa-TF pathway.
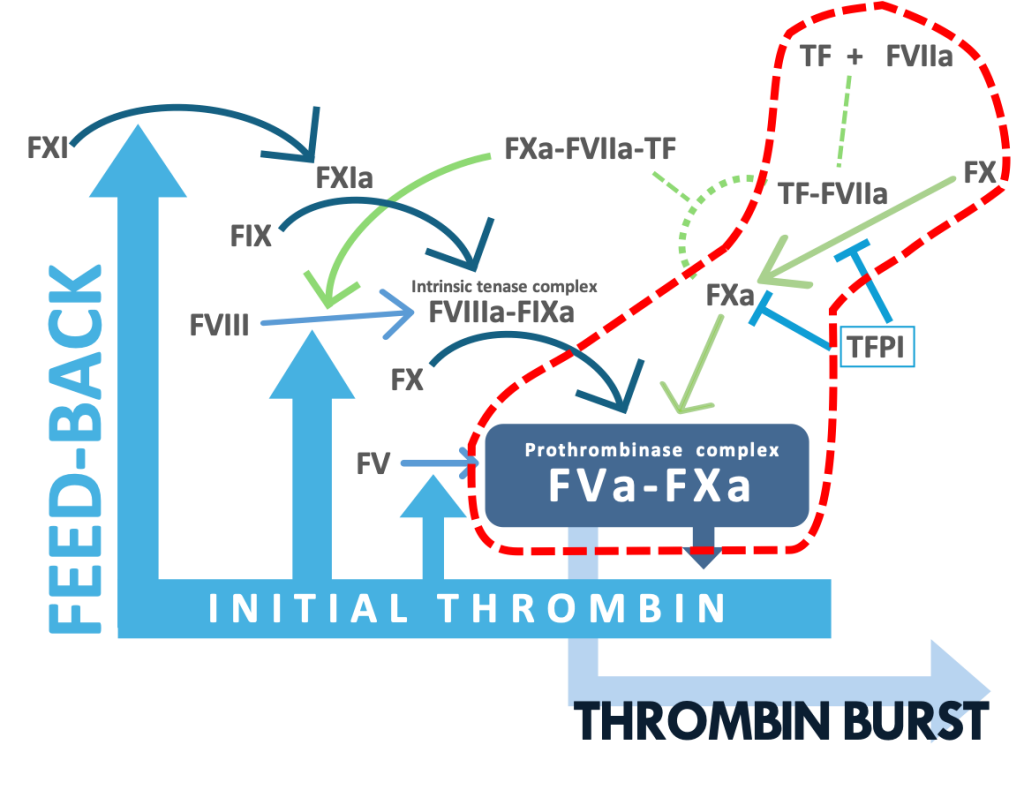
The SMAT®-FVIII kit is utilized for specifically determining the thrombin production via the FIXa-FVIIIa mechanism by which FVIII is activated by the FXa-FVIIa-TF complex. The kit may provide excellent approaches for accessing bleeding and thrombosis risks caused by the defect and increase in FVIII, respectively.
The SMAT®-APCD is intended as a non-activated blood coagulation test to explore initiators of coagulation such as TF and activated coagulation factors present in plasma. The assay can also be used for detecting procoagulant substances that are included in conditioned media of cells, body fluids, and biological products.
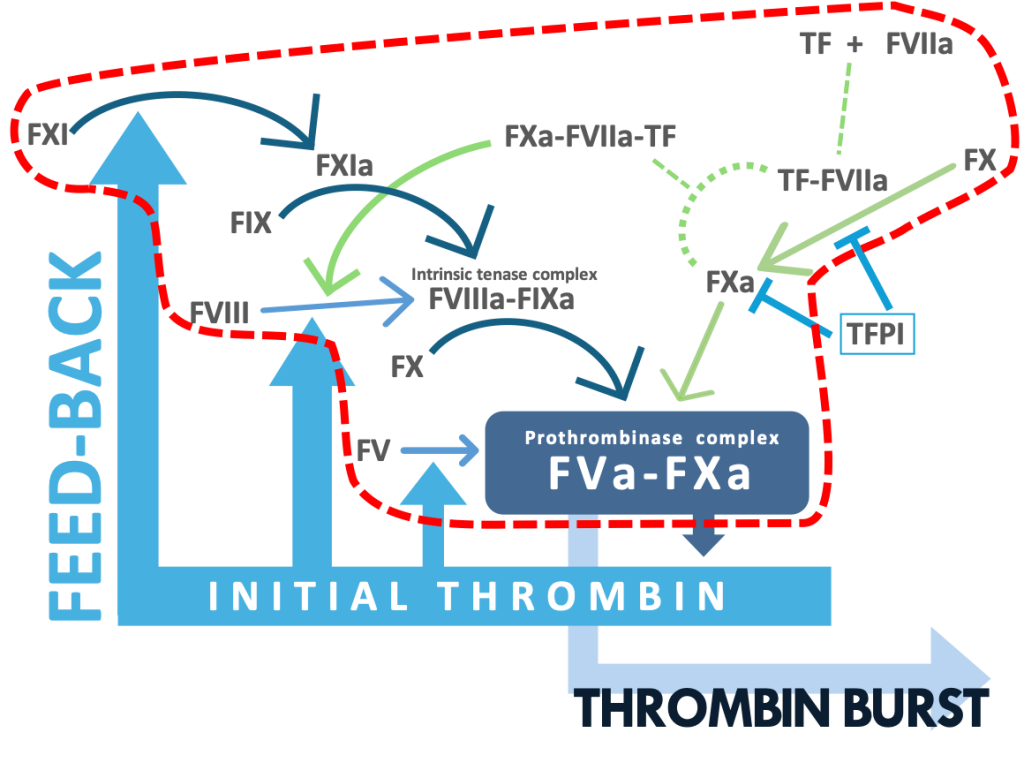
The SMAT®-TFPI, which is based on the initial TG assay, is the first coagulation test for determination of TFPI anticoagulant activity in plasma. The kit is intended to assess the profile of plasma TFPI activity in patients with thrombotic and bleeding disorders.